What is an inverter? This is simply a specialized electrical device in industry, widely used in modern machinery and equipment today. So how is the structure of the inverter? On what principle does it work? What are the benefits when applying inverters to machines? This article will help you answer these questions.
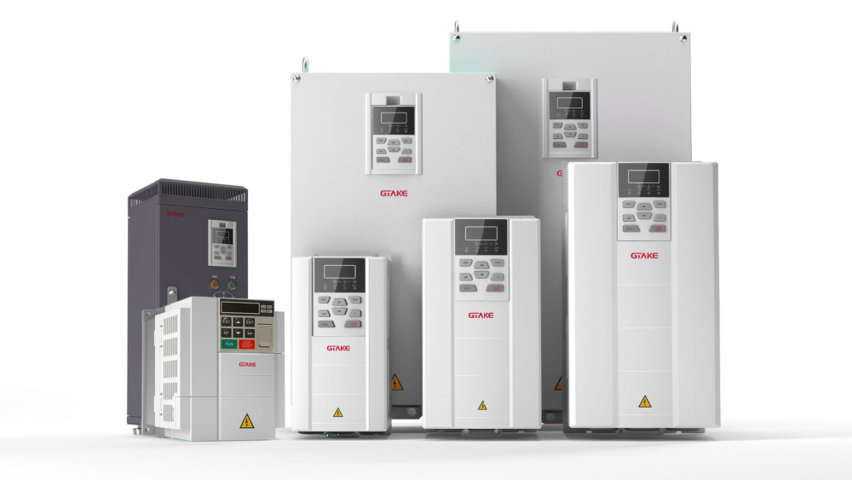

1 – What is an inverter?
An inverter is an intermediate device that converts alternating current from one frequency to alternating current at another frequency. In other words, the inverter will change the frequency of the current passing through the coil inside the motor and thereby control the motor speed from stepless and without the need for a mechanical gearbox.
Thanks to the semiconductor components inside the inverter, it will help to sequentially close and disconnect the wires inside the motor, creating a rotating magnetic field that rotates the rotor.

The inverter will be used to control the speed of the AC motor according to the frequency control method. In which the frequency of the power grid will transform into a variable frequency.
Currently, there are inverters such as AC, DC, 1-phase 220V, 3-phase 220V, 3-phase 380V, etc. In addition, there are specialized inverters for pumps, fans, cranes, elevators, etc. air conditioning system.
So, you have grasped the concept of what an inverter is, now we will start to learn about its structure.
2 – Structure inside
The inverter has an internal structure consisting of functional parts that receive a fixed frequency input voltage to change into a variable frequency voltage to help control the motor speed.
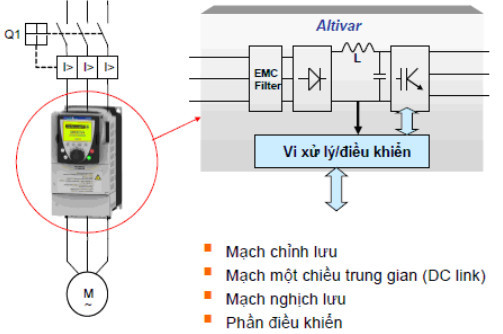
2.1 – Diode
The Diode of the inverter as well as the rectifiers commonly found in the power supply. The rectifier helps AC voltage to be converted into DC, when the rectified voltage passes through the filter capacitor array to have a flat, stable voltage, it will supply power to the IGBT inverter.
2.2 – Insulated Gate Bipolar – IGBT
The IGBT helps the inverter to switch quickly, improving efficiency. The IGBt will drive the trigger in sequence to generate pulses with different widths due to the DC Bus voltage stored in the capacitor.
2.3 – Control circuit
The control circuit of the inverter will connect to the peripheral circuit to receive the input signal to the main IC. Therefore, the inverter will be controlled according to the user’s configuration and settings.
3 – What are the other accessories of the inverter?
3.1 – AC Reactor
AC reactor is a coil wound around a steel core to help limit interference when alternating current enters. The AC reactor also helps to reduce the peak amplitude of the input spikes, thereby reducing electric shocks, helping to stabilize the AC power of the inverter and motor. Especially harmonics will be reduced, thereby helping the DC bus to be stable and increase the life of the capacitor.
3.2 – DC Reactor
The DC reactor is attached to the inverter to make the DC Bus source stable, with a large reserve of energy. In particular, the DC reactor also helps to prevent voltage drop of the input source of the inverter when powering the IGBT inverter when it is operating at full load.

3.3 – Braking resistor
The braking resistor is used for the inverter to drive the motor to run. When the inverter stops working or is braked, then the inverter will become a generator with high energy. So when the motor stops urgently, this energy source will be consumed by the discharge resistor to help that energy source.
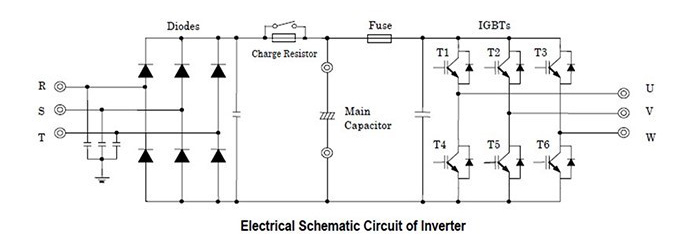
4 – What is the working principle of inverter?
The inverter has the function of turning a 1-phase or 3-phase power source into a flat DC power source. This is done by a diode bridge rectifier and a capacitor. So the input power can be 1 phase or 3 phase, because when it comes in, it will be stabilized at a fixed voltage and frequency.
DC voltage will be generated and stored in the capacitor. From there, the DC will be converted into a symmetrical 3-phase AC. This is followed by a proper self-triggering due to the IGBT converter, which will generate a 3-phase AC voltage using the PWM pulse width method.
5 – How many types of inverters are there?
Inverters are classified based on the characteristics of the current, so there are two main types of inverters as follows:
AC inverter: this is the most commonly used type, used in speed control of motors and AC motors.
DC inverter: This type is used to control branched electric motors, DC motors.
6 – What are the benefits of using an inverter?
Inverter is a widely used device and has many applications in industry and life. So the inverter has the following benefits:
+ Change engine speed and reverse rotation easily
+ Does not cause voltage drop or difficult to start when reducing the current from the motor or from the star delta.
+ Because the motor does not have to carry a large load when suddenly starting, it will avoid damage to the mechanical part, the bearing, and increase the life of the motor.
+ Helps save energy.
+ Helps the system operate safely because the inverter will protect electronic equipment from overcurrent, overvoltage and undervoltage.
+ The inverter is also used in communication modules, making it easier to control and monitor from the center.
A reputable inverter supplier
VPIC is the number one prestigious supplier of inverter equipment in Vietnam. We specialize in distributing industrial inverters from major brands in the world such as Fuji, Inovance, Danfoss, etc.
With a large distribution system, we are always ready to provide quality inverter products, quickly and in a timely manner. At the same time, VPIC also provides professional technical services such as:
+ Design and construction of electrical systems, consulting and providing optimal solutions
+ Maintain equipment, handle system errors at the factory
+ Repair and restore damaged equipment.
If you have any need to buy or cooperate, please contact Hotline: 0896 422 224
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt